Purchasing a home is one of the most significant financial commitments many individuals make in their lifetime. A critical factor influencing homeownership affordability is the mortgage rate. Nationwide mortgage rates fluctuate due to various economic and financial influences, affecting both prospective homebuyers and those looking to refinance their existing loans. Understanding current mortgage rate trends is crucial for making well-informed borrowing decisions. This article provides a comprehensive analysis of nationwide mortgage rates, highlighting key factors that influence them, recent market trends, and insights into the future of mortgage rates in the U.S.
Factors Influencing Nationwide Mortgage Rates
1. Economic Conditions and Inflation
The overall health of the economy plays a fundamental role in determining mortgage rates. Economic indicators such as the Gross Domestic Product (GDP), employment levels, and consumer spending significantly impact interest rates. Inflation is another crucial factor; when inflation rises, lenders often increase mortgage rates to compensate for the diminishing purchasing power of money. The Federal Reserve closely monitors inflation trends and adjusts monetary policies accordingly, which in turn affects mortgage interest rates nationwide.
2. Federal Reserve Policies
The Federal Reserve does not set mortgage rates directly, but its policies have a significant influence on them. By adjusting the federal funds rate, the Fed impacts short-term interest rates, which subsequently influence long-term mortgage rates. During economic downturns, the Federal Reserve may lower interest rates to stimulate borrowing, while in periods of high inflation, it may increase rates to curb excessive spending. Homebuyers and investors closely monitor Federal Reserve meetings and policy announcements to anticipate future mortgage rate movements.
3. Housing Market Demand and Supply
The real estate market’s supply and demand dynamics also affect mortgage rates. When housing demand is high, lenders may increase interest rates due to increased loan applications. Conversely, when demand slows down, lenders might lower rates to attract more borrowers. Factors such as population growth, urban development, and government housing policies influence the supply and demand equilibrium in the housing market, ultimately impacting mortgage rates.
4. Credit Scores and Borrower Profiles
While nationwide mortgage rates provide a general benchmark, the actual rate a borrower qualifies for depends on individual financial factors. Credit scores, debt-to-income ratios, employment stability, and loan-to-value ratios all play a crucial role in determining interest rates. Borrowers with excellent credit scores typically receive lower mortgage rates compared to those with lower scores. Lenders assess the risk associated with each borrower before finalizing interest rates on loans.
5. Loan Types and Terms
Different types of mortgage loans come with varying interest rates. Fixed-rate mortgages, for instance, have stable interest rates throughout the loan term, while adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMs) have fluctuating rates based on market conditions. Loan terms also influence interest rates—shorter-term loans (such as 15-year mortgages) usually have lower rates than longer-term loans (such as 30-year mortgages). Understanding these variations can help borrowers choose the best loan option based on their financial situation and long-term goals.
Recent Trends in Nationwide Mortgage Rates
Mortgage Rates in 2024
As of 2024, mortgage rates have experienced volatility due to ongoing economic shifts. After the aggressive rate hikes by the Federal Reserve in 2022 and 2023 to combat inflation, the real estate market saw fluctuating mortgage rates. While some months showed declining rates due to cooling inflation, economic uncertainty kept rates higher than pre-pandemic levels. Analysts predict that rates may continue to be influenced by Federal Reserve decisions, employment data, and housing market trends.
Regional Variations in Mortgage Rates
Mortgage rates vary across different states and regions due to local economic conditions, housing demand, and lender policies. In highly competitive real estate markets like California, New York, and Florida, rates may be slightly higher due to increased demand for loans. Meanwhile, states with slower housing market growth may see lower mortgage rates. Borrowers should compare lender offers from different regions to secure the best possible rate.
The Impact of Technology and Online Lenders
The rise of online mortgage lenders has increased competition, giving borrowers more options to compare and secure better rates. Digital platforms provide instant loan estimates, making it easier for consumers to shop around for the most favorable mortgage rates. Fintech innovations have also streamlined the mortgage approval process, allowing faster transactions and better customer experiences.
Future Outlook: Where Are Mortgage Rates Headed?
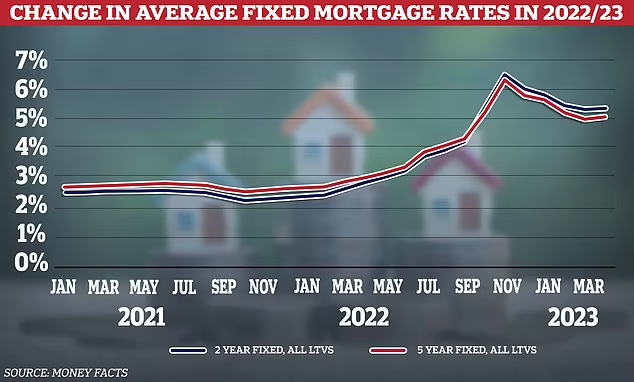
Predicting future mortgage rate movements requires analyzing economic trends, Federal Reserve policies, and global financial developments. While some experts anticipate a gradual decline in rates as inflation stabilizes, others suggest that high borrowing costs may persist if economic uncertainty remains. Homebuyers and investors should stay informed about interest rate trends and work with mortgage professionals to secure the best financing options.
Tips for Securing the Best Mortgage Rate
- Improve Your Credit Score – A higher credit score increases your chances of qualifying for lower mortgage rates. Pay off debts, make timely payments, and avoid unnecessary credit inquiries to boost your score.
- Shop Around and Compare Lenders – Different lenders offer varying mortgage rates and terms. Obtain quotes from multiple financial institutions to find the best deal.
- Consider a Shorter Loan Term – Shorter-term mortgages often come with lower interest rates. If financially feasible, opting for a 15-year mortgage instead of a 30-year term can save you money in interest payments.
- Make a Larger Down Payment – A higher down payment reduces the loan amount and may qualify you for better interest rates. Many lenders offer lower rates for borrowers who put down 20% or more.
- Lock in a Good Rate – If you find a favorable mortgage rate, consider locking it in to protect yourself from potential rate increases in the near future.
Conclusion
Nationwide mortgage rates are a crucial aspect of the home-buying process, affecting affordability and long-term financial planning. Understanding the factors influencing mortgage rates, staying updated on trends, and implementing strategies to secure the best rates can help borrowers make informed decisions. Whether you’re a first-time homebuyer, refinancing an existing loan, or investing in real estate, staying informed about mortgage rate movements is key to financial success. Always research and consult professionals before making significant borrowing commitments to ensure you secure the most favorable mortgage terms.
Read more: March Birthstone: Aquamarine’s Beauty and Meaning
FAQ’s Section
Nationwide mortgage rates are primarily influenced by economic conditions, Federal Reserve policies, inflation, and housing market trends. Individual borrower factors like credit scores also play a role.
Mortgage rates can change daily or even multiple times a day, depending on market fluctuations, economic data releases, and Federal Reserve policy decisions.
No, different lenders offer varying mortgage rates based on their lending policies, operational costs, and risk assessments. It’s essential to compare offers from multiple lenders.
Yes, borrowers can negotiate mortgage rates with lenders, especially if they have strong credit scores, a solid financial history, and competitive loan offers from other institutions.
A good mortgage rate depends on current market conditions, the type of loan, and the borrower’s financial profile. Checking daily rate updates and consulting with mortgage professionals can help determine a competitive rate.


